Search engine optimization, or SEO, is no longer optional. It is a core skill for anyone who wants visibility online. In 2026, SEO sits at the intersection of technology, content, user experience, and brand trust. This guide explains SEO from the ground up for beginners. It focuses on how SEO actually works today, not outdated tactics.
What is Search Engine Optimization and Why It Matters Today
What Is SEO
SEO is the process of improving a website so that search engines can find, understand, and rank it for relevant queries. The goal is to earn organic traffic. Organic traffic means visitors who arrive through unpaid search results.
SEO is not about tricking search engines. It is about helping them deliver better results to users.
At its core, SEO answers three questions:
- Can search engines access your site?
- Can they understand what your pages are about?
- Do they trust your site enough to rank it highly?
Why Search Engine Optimization Matters in 2026
Search engines remain the primary way people discover information, products, and services. Despite the growth of social platforms and AI tools, search still drives high-intent traffic.
SEO matters because:
- Organic search delivers consistent traffic over time.
- Users trust organic results more than ads.
- SEO supports every stage of the buyer journey.
- SEO compounds. Good work today pays off later.
In 2026, SEO also affects visibility inside AI-generated answers, shopping results, maps, and voice assistants. If you are not optimizing for search, you are invisible in many digital spaces.

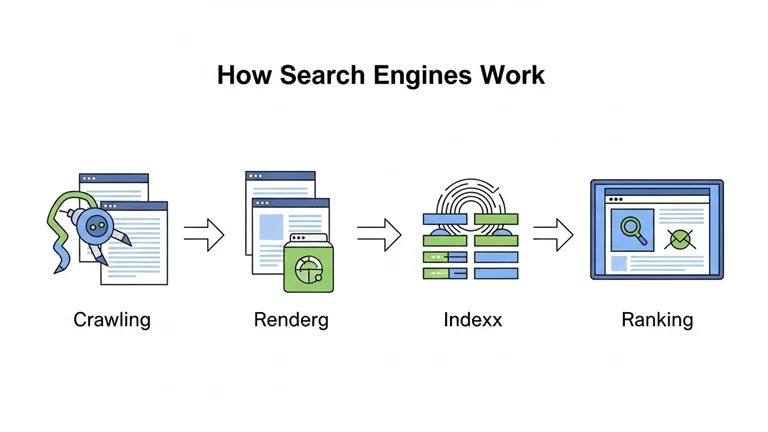
How Search Engines Work
Search engines follow a structured process to deliver results. Understanding this process helps you make better SEO decisions.
Crawling
Crawling is how search engines discover content.
Search engines use automated programs called crawlers or bots. These bots follow links across the web. They visit pages, read their content, and find new links.
Crawling depends on:
- Internal linking
- External links
- Site architecture
- Crawl budget
- Robots.txt rules
If a page cannot be crawled, it cannot rank.
Rendering
Rendering is how search engines process a page.
Modern websites rely on JavaScript. Search engines must render the page to see the final content users see. This includes text, images, menus, and interactive elements.
Rendering issues can hide content from search engines. Poor rendering can break SEO even if the content is good.
Indexing
Indexing is the process of storing pages in a search engine’s database.
Once a page is crawled and rendered, the search engine decides whether to index it. Indexed pages are eligible to appear in search results.
Pages may not be indexed due to:
- Duplicate content
- Thin or low-value content
- Technical errors
- Noindex tags
Ranking
Ranking is the process of ordering results for a search query.
Search engines use complex algorithms. These algorithms evaluate hundreds of signals. The goal is to show the most relevant and useful result.
Key ranking factors include:
- Search intent match
- Content quality
- Page experience
- Authority and trust
- User engagement signals
Ranking is dynamic. Results change based on query context, location, device, and user behavior.
Search Engine Optimization vs SEM vs PPC
SEO
SEO focuses on organic visibility. You do not pay for clicks. You earn rankings through optimization and authority.
Example:
A blog post ranking for “SEO basics” that brings traffic every month without ad spend.
SEM
SEM stands for search engine marketing. It includes SEO and paid search strategies.
SEM is the broader discipline of gaining visibility in search engines.
PPC
PPC stands for pay-per-click advertising. You pay when someone clicks your ad.
Example:
A Google Ads campaign targeting “buy running shoes” where each click costs money.
Key Differences
- SEO is long-term. PPC is immediate.
- SEO builds assets. PPC stops when budget stops.
- SEO improves trust. PPC provides placement.
Most businesses use both. Search engine optimization builds sustainable growth. PPC fills short-term gaps.

Why Search Engine Optimization Is Important: Data and Reality
Search engine optimization is supported by strong data.
Key facts that still hold in 2025:
- Organic search drives over 50% of website traffic on average.
- The first five organic results receive most clicks.
- Users often skip ads for informational searches.
- SEO leads convert better than many other channels for non-brand queries.
SEO also reduces dependency on paid platforms. Algorithm changes affect all channels, but owned search visibility is more stable than rented traffic.
How User Behavior Has Changed
Mobile-First Behavior
Most searches now happen on mobile devices. Google uses mobile-first indexing. This means the mobile version of your site is the primary version evaluated.
Implications:
- Responsive design is mandatory.
- Page speed matters more.
- Content must be readable on small screens.
Voice-Search
Voice search continues to grow through phones, cars, and smart devices.
Voice queries are:
- Longer
- More conversational
- Often question-based
SEO must address natural language and clear answers.
AI-Assisted Search
Search engines now integrate AI-generated summaries and answers. Users often get answers without clicking.
This changes SEO goals:
- Visibility matters even without clicks.
- Structured content increases inclusion.
- Brand mentions matter alongside links.
SERP Features and Why They Matter
Search engine results pages (SERPs) are no longer ten blue links.
Common SERP features include:
- Featured snippets
- People Also Ask
- Knowledge panels
- Local packs
- Image and video carousels
- Shopping results
These features affect click behavior.
Why they matter:
- They push organic results down.
- They offer alternative visibility.
- They reward clear, structured content.
Optimizing for SERP features is now part of SEO basics.
Main Types of SEO
SEO has several core components. Each serves a different purpose.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures search engines can access and process your site.
Key areas:
- Site architecture
- Page speed
- Mobile usability
- Indexing control
- Structured data
- Core Web Vitals
- Security (HTTPS)
Technical SEO is foundational. Without it, other efforts fail.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on individual pages.
Key elements:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Headings
- URL structure
- Internal links
- Content relevance
- Media optimization
On-page SEO aligns content with search intent.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO builds authority outside your site.
Main factors:
- Backlinks
- Brand mentions
- Digital PR
- Reviews
- Social signals (indirect)
Off-page SEO signals trust and credibility.
Content Optimization for Users and Search Engines
Content is the core of SEO.
Good content:
- Solves a problem
- Matches search intent
- Is easy to read
- Is accurate and current
Optimization principles:
- One primary topic per page
- Clear headings
- Simple language
- Logical structure
- Supporting media when useful
Avoid keyword stuffing. Use keywords naturally. Focus on clarity first.
Understanding E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Experience
Content should reflect real experience.
Example:
A product review written by someone who used the product.
Expertise
The creator should demonstrate knowledge.
Example:
An SEO guide written by someone with hands-on SEO work.
Authoritativeness
The site and author should be recognized.
Example:
Mentions from reputable sites or industry publications.
Trustworthiness
The site should be transparent and reliable.
Signals include:
- Clear author information
- Accurate content
- Secure site
- Honest policies
E-E-A-T is not a single ranking factor. It is a quality framework used by search engines.
Generative Engine Optimization and AI Visibility
Generative engine optimization focuses on visibility in AI-driven answers.
AI systems pull information from trusted sources. They favor:
- Clear structure
- Factual accuracy
- Strong entity associations
- Consistent brand signals
To improve AI visibility:
- Use clear definitions
- Answer questions directly
- Build topical authority
- Strengthen brand mentions
SEO in 2026 includes optimizing for humans, search engines, and AI systems.
Link Building and Brand Authority
Links remain important, but their role has changed.
Quality matters more than quantity.
Effective link building focuses on:
- Editorial links
- Relevant sources
- Brand mentions
- Real relationships
Tactics that still work:
- Publishing useful content
- Digital PR
- Data-driven studies
- Thought leadership
Avoid manipulative link schemes. They carry risk and little long-term value.
SEO Specialties
SEO adapts to different contexts.
Ecommerce SEO
Focus areas:
- Product pages
- Category structure
- Reviews
- Structured data
- Crawl efficiency
Local SEO
Focus areas:
- Google Business Profile
- Local citations
- Reviews
- Location pages
- Maps visibility
International SEO
Focus areas:
- Hreflang tags
- Country targeting
- Language localization
- Cultural context
Enterprise SEO
Focus areas:
- Scale
- Governance
- Automation
- Cross-team coordination
- Advanced analytics
News SEO
Focus areas:
- Speed
- Indexing
- Structured data
- Freshness
- Publisher authority
How SEO Works Step by Step
Research
Research defines direction.
Tasks include:
- Keyword research
- Search intent analysis
- Competitor analysis
- Audience understanding
Planning
Planning turns data into action.
Tasks include:
- Site structure planning
- Content mapping
- Technical fixes prioritization
- Resource allocation
Execution
Execution is implementation.
Tasks include:
- Publishing content
- Optimizing pages
- Fixing technical issues
- Building links
Monitoring
Monitoring tracks performance.
Key metrics:
- Rankings
- Organic traffic
- Click-through rates
- Indexing status
- Engagement
Reporting
Reporting turns data into insight.
Reports should explain:
- What changed
- Why it changed
- What to do next
SEO is iterative. It improves through continuous adjustment.
SEO Tools Beginners Should Use
Google Search Console
Search Console shows how Google sees your site.
Key uses:
- Indexing issues
- Search queries
- Clicks and impressions
- Technical errors
Google Analytics
Analytics tracks user behavior.
Key uses:
- Traffic sources
- Engagement metrics
- Conversion tracking
Keyword Research Tools
Beginner-friendly options include:
- Google Keyword Planner
- Search Console query data
- Third-party tools for keyword ideas
Tools support decisions. They do not replace thinking.
How SEO Evolves With Technology and Society
SEO reflects how people search.
Key drivers of change:
- New devices
- Faster networks
- AI systems
- Privacy regulation
- Changing content formats
SEO fundamentals remain stable:
- Accessibility
- Relevance
- Trust
- User satisfaction
Tactics change. Principles persist.
SEO as a Career and Service
SEO is a viable long-term career.
Roles include:
- SEO specialist
- Technical SEO
- Content SEO
- SEO strategist
- SEO consultant
SEO services are in demand because:
- Search remains critical
- Businesses need expertise
- Algorithms are complex
Good SEO professionals combine analytical skills, writing clarity, and technical understanding.
How to Learn SEO From Scratch
Step 1: Learn the Fundamentals
Understand:
- How search engines work
- Basic ranking factors
- SEO terminology
Step 2: Practice on a Real Site
Theory is not enough.
- Start a simple website
- Use Search Console
- Publish content
- Track results
Step 3: Study Real Search Results
Analyze:
- Top-ranking pages
- SERP features
- Content formats
Step 4: Learn Technical Basics
Focus on:
- HTML basics
- Site speed
- Mobile usability
Step 5: Stay Updated
Follow:
- Official search engine documentation
- Reputable SEO publications
- Case studies
SEO rewards consistent practice, not shortcuts.
Practical Takeaway
SEO in 2026 is about clarity, usefulness, and trust at scale. Start by ensuring your site works technically. Publish content that directly answers real questions. Use data to guide decisions. Monitor performance and adjust regularly. SEO is not a one-time task. It is a system. Build it step by step, and results follow.